Mẹo Prevention, appraisal, internal and external failure costs are detailed on a(n)
Thủ Thuật Hướng dẫn Prevention, appraisal, internal and external failure costs are detailed on a(n) Mới Nhất
Họ tên bố(mẹ) đang tìm kiếm từ khóa Prevention, appraisal, internal and external failure costs are detailed on a(n) được Cập Nhật vào lúc : 2022-12-10 04:08:03 . Với phương châm chia sẻ Mẹo Hướng dẫn trong nội dung bài viết một cách Chi Tiết 2022. Nếu sau khi Read Post vẫn ko hiểu thì hoàn toàn có thể lại phản hồi ở cuối bài để Mình lý giải và hướng dẫn lại nha.To collect quality costs an organization needs to adopt a framework to classify costs. CoQ is usually understood as the sum of conformance plus non-conformance costs, where cost of conformance is the… Expand
Nội dung chính Show- Effects of Construal Level on the Price-Quality RelationshipQuality Without Tears : The Art of Hassle-Free ManagementWhy Cost of Poor Quality (COPQ)Categories of Cost of QualityWhen to use Cost of Poor Quality (COPQ)Steps in implementing Cost of Poor Quality (COPQ)Example of Cost of Poor Quality (COPQ)Cost of Poor Quality TemplateUnlock Additional Members-only Content!Why Pursue a Six Sigma Level of Quality / Excellence?Avoid ErrorsDisadvantages of Cost of Poor Quality (COPQ)Cost of Poor Quality (COPQ) VideosVideos on the Economic Considerations of QualityCost of Poor Quality (COPQ) BooksQuality is FreeBusiness @ Speed of ThoughtSix Sigma Black Belt Certification Cost of Poor Quality Questions:Unlock Additional Members-only Content!Unlock Additional Members-only Content!What are prevention and appraisal costs?What are internal and external failure costs?What is prevention appraisal failure?What does prevention cost include?
- View 3 excerpts, references background
Effects of Construal Level on the Price-Quality Relationship
Drawing on construal level theory, this research proposes that consumers' reliance on price (vs. feature-specific product attributes) for making quality inferences will be enhanced when the judgment… Expand
- View 1 excerpt, references background
Quality Without Tears : The Art of Hassle-Free Management
Now available in trade paperback, this mega-seller brings the timeless message of "the leading evangelist of quality" (as Time called Philip Crosby) to an ever-widening audience. Drawing on quality… Expand
Cost of Poor Quality (COPQ) is the cost associated with providing poor quality products or services to the customer. In other words, it is the total financial losses incurred by the company due to performing incorrect things. For example, scrap, rework, repair, warranty failure.
Cost of Quality is a methodology used in the organization to measure the amount of resources being used for the cost of good quality. In other words, it is the cost of achieving quality products or services.
Cost of quality is the combination of cost of good quality and cost of poor quality.
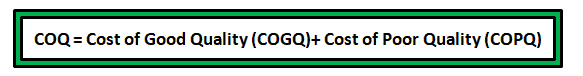
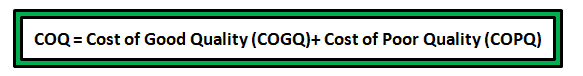
Why Cost of Poor Quality (COPQ)
- COPQ tells how profit is affected by the qualityIt speaks the language of managementHelps to prioritize improvement actionsOptimize the resources and also helps in identify wastes in the systemImproves continuous improvement culture
Categories of Cost of Quality
Cost of quality can be divided into four categories: prevention cost, appraisal cost, internal failure cost, and external failure cost.
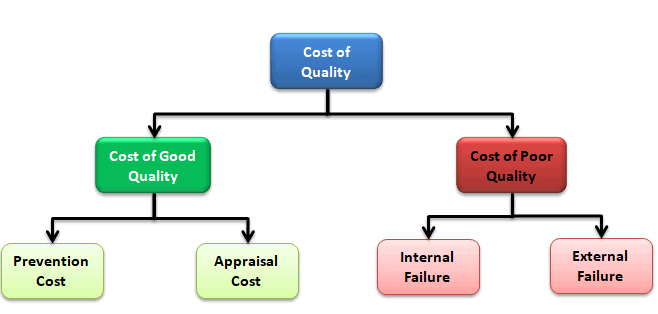
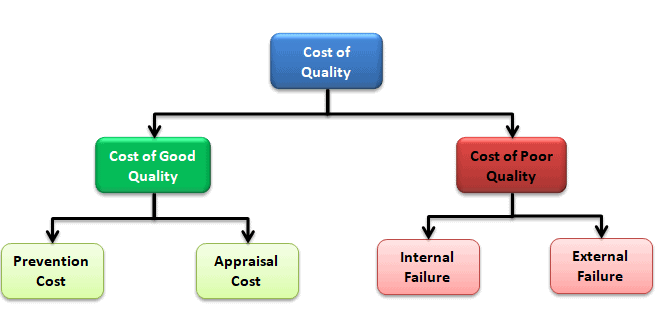
Preventive Cost– Preventive costs are the costs of the activities specially designed to prevent poor quality of products or services. In other words, efforts are related to preventing failures.
- Quality planningContract reviewTrainingsQuality auditsSupplier evaluationMarket researchProcess capability studies
Appraisal costs – Appraisal costs are the costs incurred due to those activities which are performed to detect the poor quality of product or services. In other words, appraisal costs are related to testing, measuring, and auditing. The appraisal cost focuses on the discovery of defects rather than the prevention of defects.
- Incoming goods inspectionIn-process inspectionSupplier inspectionLaboratory testingFinal goods inspectionCalibration
Internal failure – Internal failure costs result from the identification of defects prior to delivery of the product or service to the customers. In addition, these are the costs due to the failure of a product to achieve required quality standards.
- ReworkRepairInternal scrapRe-testingEfforts spent on failure analysisRaw material rejectionIn-process rejection
External failure – External failure costs arise from the rejection of the product or services by the customers after delivery. In other words, these are the costs when a product or service fails to meet the required quality standards and is detected after it reaches the customer.
- Warranty claimsCustomer visitsPenaltiesReplacementsInvestigationsLoss of goodwill
When to use Cost of Poor Quality (COPQ)
Organizations use COPQ to understand the opportunities to improve the quality by reducing internal and external failure costs. Basically, by increasing the expenditure on prevention.
Steps in implementing Cost of Poor Quality (COPQ)
- Define the organization quality goals and objectivesEstimate the current capabilities of machines, systems, and processesCollect data for prevention cost, appraisal cost, internal failure cost and external failure costValidate the quality cost data with financePareto the quality costs and prioritize the actionsImplement the corrective actions such as automate the quality audits, streamline the inspection process, implement Poka-Yoke etc.,Compare the quality costs before and after process improvement (as shown below)Finally, present the quality cost improvements to top management.
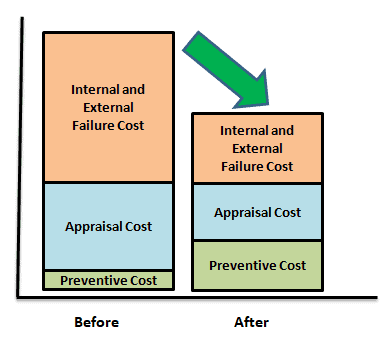
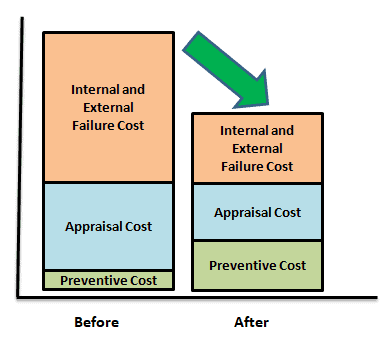
Example of Cost of Poor Quality (COPQ)
Quality assurance is everything for an organization. Incorporating Six Sigma and other Lean tools, this allows companies to decrease waste (Raw materials, Logistics costs, and unnecessary man hrs) which increases their bottom line.
Let’s say you are running a DMAIC project. In the define phase, you want to quantify the cost of poor quality. You start by defining what a defect is, then measuring how many defects per million opportunities your process has. (You would use this same material to create your baseline sigma in the measure phase, next.)
Example: Imagine producing TVs and for every 1M produced 2% were damaged… That’s 20,000 TVs. If those damages were not salvageable, and it cost $100 to produce each unit, then it cost your company 20k *$100 = $2 Million
But that’s not all. How many people would you work on re-inspection, warranty repair, supplier evaluation etc.? Here you go for the breakup of the costs. Below are the split-up of various costs (Just as an example).
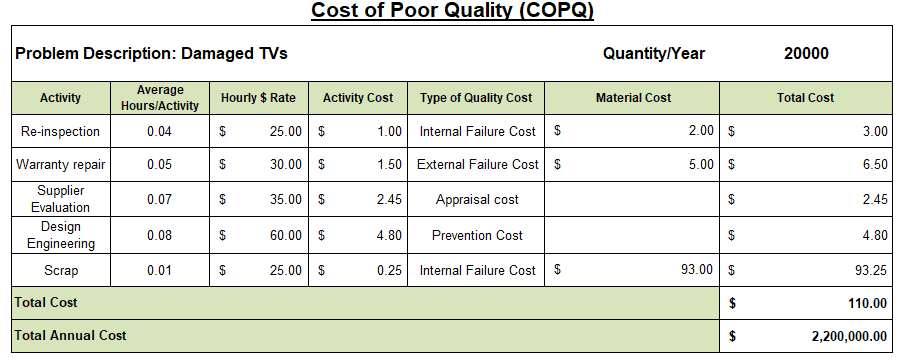

Total material cost is $100 unit and an additional $10 per unit spent on quality costs. At 20k units, that is $200k. The total cost to the company would be $2.2 Million!
Cost of Poor Quality Template
Unlock Additional Members-only Content!
To unlock additional content, please upgrade now to a full membership.Upgrade to a Full Membership
If you are a thành viên, you can log in here.
Why Pursue a Six Sigma Level of Quality / Excellence?
Let’s use the same example. At a Six Sigma level you would only produce 3.4 defects per million opportunities. In the previous example the process was making 20,000 defects per million. Moving to a six sigma level of quality would mean 19,996.6 less defects per million units made! That’s a savings of $2.2M – (3.4 * $110) = $2.2M – $374 … so, nearly $2.2 Million!
Avoid Errors
The best in any field figured out how to avoid errors very early on. We should, too, if we want to engineer a great process.
For example, Simon Ramo notes that among the very best tennis players, to win you need good winning shots; to be a good average player, you need to merely lower your failure rate. In expert tennis, 80% of the points are won, while in amateur tennis, 80% are lost. The same is true for wrestling, chess, and investing: beginners should focus on avoiding mistakes, experts on making great moves. – Erik Falkenstein, Author The Missing Risk Premium
“The most important thing to do if you find yourself in a hole is to stop digging.”
Warren BuffettDisadvantages of Cost of Poor Quality (COPQ)
- Financial lossSchedule delayNeed more controls and checksUnnecessary spent on resourcesLeads to associates de-motivationReputation stakeCompetitors take advantage
Cost of Poor Quality (COPQ) Videos
Ironically, this video has poor sound quality, but the content is good.
Videos on the Economic Considerations of Quality
Cost of Poor Quality (COPQ) Books
Quality is Free
Like every other human domain, we need to identify what the problem is before we can fix it. And that doesn’t always happen in business.
“The first erroneous assumption is that quality means goodness, or luxury, so shininess, or weight. We must define quality as conformance to requirements if we are to manage it. The second erroneous assumption is that quality is an intangible and therefore not measurable. In fact, quality is precisely measurable by the oldest and most respected of measurements – cold hard cash. It is much less expensive to prevent errors than to rework, scrap or service them.” – Quality is Free
The book has a quality improvement program that can be installed in any service or manufacturing company.
Business @ Speed of Thought
I list this here because Bill Gates’ Business @ the Speed of Thought is influenced by Crosby’s Quality is Free work. It may resonate a little better with modern audiences as the case studies are newer – despite being 16 years old in 2015. But you can see the basic concepts of Quality is Free represented here.
- There is no reason for having errors or defects in any product or service.Businesses are slow to change because we reject newness.How you come across to others should not be left to chance. Quality products and services is something you can control.It is much less expensive to prevent errors than to have rework.
Also See
Hidden vs Visible Costs
Six Sigma Black Belt Certification Cost of Poor Quality Questions:
Question: Which of the following best describes internal failure costs? (Taken from ASQ sample Black Belt exam.)
(A) The economic costs associated with a catastrophic failure of an internal subsystem.
(B) The unavoidable quality system costs associated with the production of any product or service.
(C) The opposite of external failure costs.
(D) The costs resulting from a nonconformance detected before a product or service is provided.
Answer:
Unlock Additional Members-only Content!
To unlock additional content, please upgrade now to a full membership.Upgrade to a Full Membership
If you are a thành viên, you can log in here.
Question: Which of the following will have the most influence on consumers’ perception of quality?
(A) Industry standards
(B) Company financial performance
(C) Audit results
(D) Service and repair policies
Answer:
Unlock Additional Members-only Content!
To unlock additional content, please upgrade now to a full membership.Upgrade to a Full Membership
If you are a thành viên, you can log in here.
Authors
Ted Hessing
I originally created SixSigmaStudyGuide.com to help me prepare for my own Black belt exams. Overtime I've grown the site to help tens of thousands of Six Sigma belt candidates prepare for their Green Belt & Black Belt exams. Go here to learn how to pass your Six Sigma exam the 1st time through!
What are prevention and appraisal costs?
Prevention Cost – costs associated with activities specifically designed to prevent poor quality in products. Appraisal Cost – costs associated with activities specifically designed to measure, inspect, evaluate or audit products to assure conformance to quality requirements.What are internal and external failure costs?
Internal failure costs are costs associated with defects found before the customer receives the product or service. External failure costs are costs associated with defects found after the customer receives the product or service.What is prevention appraisal failure?
314 The prevention-appraisal-failure model. Failure costs - internal. The costs arising within the manufacturing organization of the failure to achieve the quality specified. Note: The term can include the cost of scrap, rework and reinspection, and also consequential losses within the organization.What does prevention cost include?
Typical prevention costs are incurred in activities such as preventing a problem from occurring and recurring, implementing the improvement process, quality related training, training for improving culture and attitudes, job related training, development and implementing a quality data and reporting system, quality ...
Post a Comment